Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a genetic disorder that affects thousands of families worldwide. It primarily impacts boys, causing muscle degeneration and weakness over time. Understanding what DMD entails is crucial for those diagnosed, their loved ones, and the broader community.
This condition can sound daunting, but knowledge empowers us. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy—from its symptoms and causes to diagnosis and treatment options. Whether you’re seeking information for yourself or someone close to you, this guide aims to shed light on how individuals with DMD navigate life while offering resources and support available in the journey ahead.
Table of Contents
What is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy?
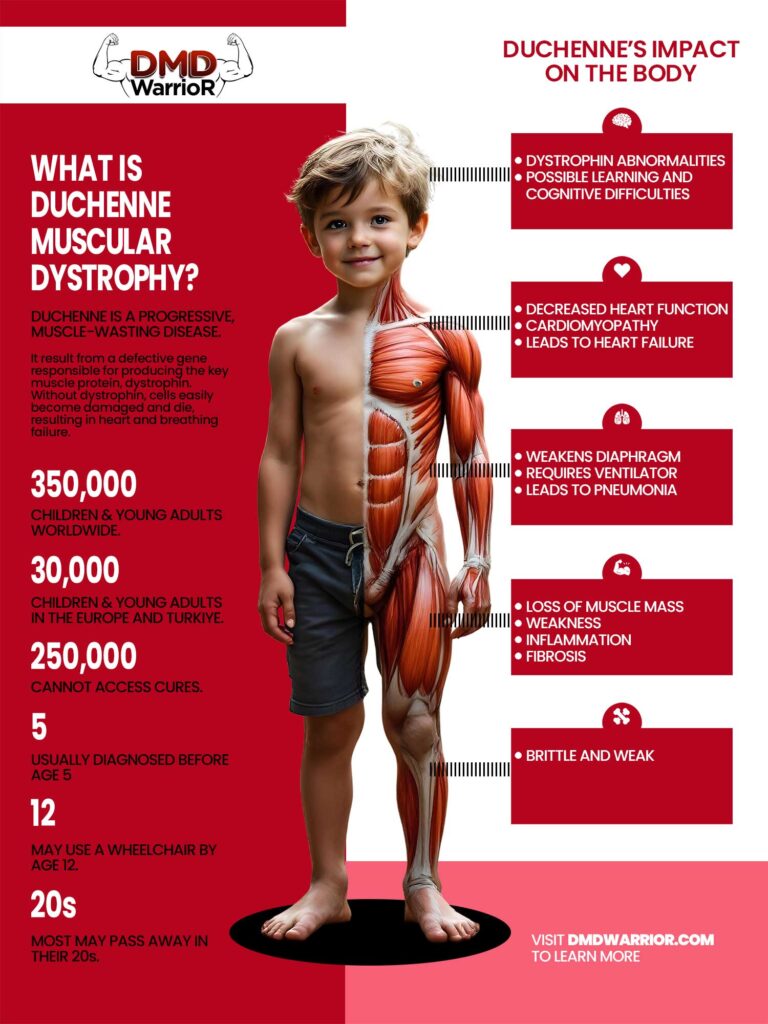
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is a severe form of muscular dystrophy caused by a mutation in the dystrophin gene. This gene plays a crucial role in maintaining muscle cell integrity. Without functional dystrophin, muscles gradually weaken and degenerate.
Typically diagnosed in early childhood, DMD primarily affects boys due to its X-linked inheritance pattern. Symptoms often appear between ages 2 and 6, with children experiencing difficulty walking, frequent falls, and challenges with physical activities.
As the condition progresses, it impacts not just mobility but also vital organs such as the heart and lungs. Children may require assistance as their independence diminishes over time. Understanding what Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy encompasses helps families prepare for the journey ahead while navigating available treatment options and support systems.
Overview
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy that primarily affects boys. This genetic disorder leads to progressive muscle degeneration and weakness due to the absence of dystrophin, a protein essential for maintaining muscle cell integrity.
DMD typically manifests in early childhood, with symptoms often appearing between ages 2 and 6. Children may have difficulty walking or climbing stairs, leading to frequent falls. As the condition progresses, mobility becomes increasingly limited.
The impact of Duchenne extends beyond physical challenges. It significantly influences emotional well-being and social interactions for both patients and their families. Understanding this disorder is crucial for effective management and support throughout its course. Awareness can lead to better resources and advocacy efforts aimed at improving quality of life for those affected by DMD.
Symptoms of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
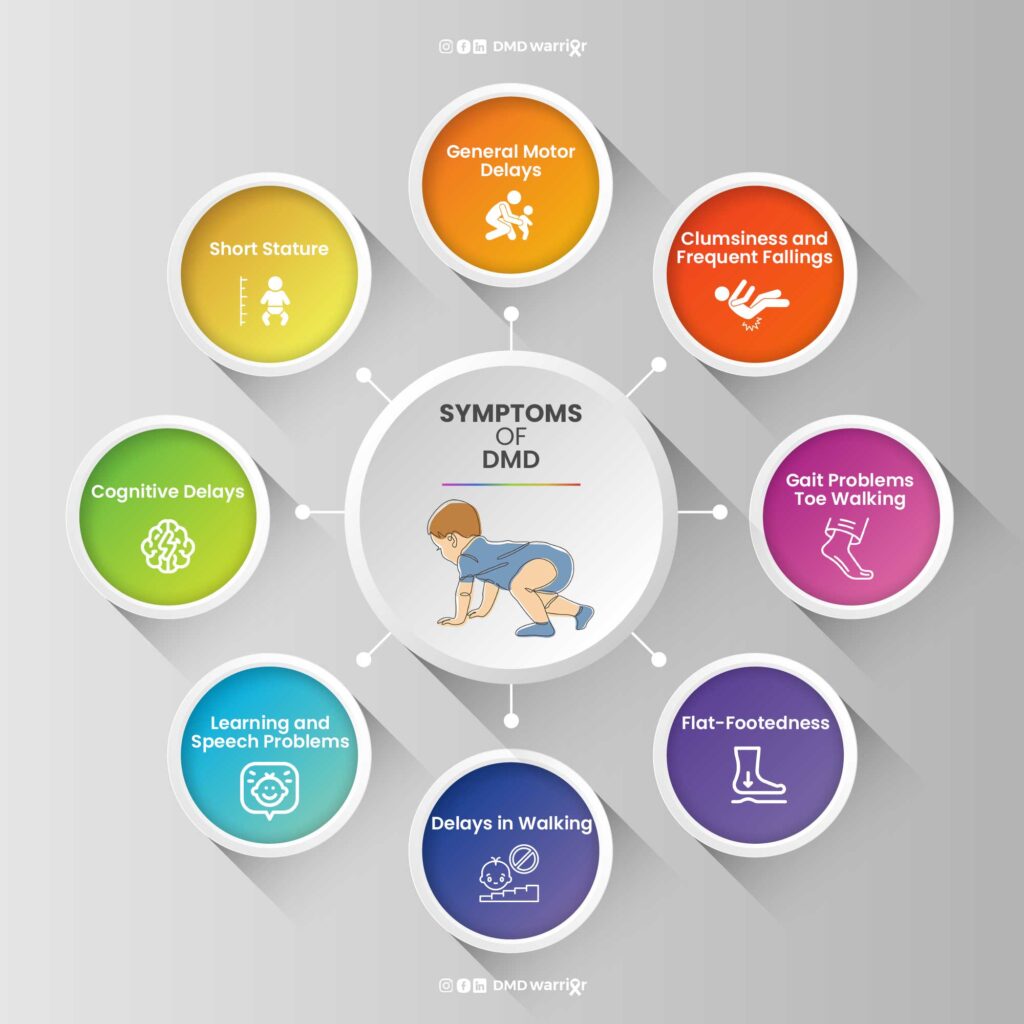
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy primarily affects boys, and its symptoms typically surface between ages 2 and 6. One noticeable sign is delayed motor skills. A child might struggle to walk or run compared to peers.
Muscle weakness often begins in the hips, pelvis, and thighs. This can lead to difficulties with activities like climbing stairs or standing from a seated position. As the condition progresses, the arms and shoulders may also weaken.
Another common symptom is an unusual posture due to muscle imbalances. Children may develop a waddling gait as their leg muscles weaken further.
As Duchenne advances, it can affect heart and respiratory muscles too. Patients might experience fatigue more quickly than others during physical activity.
Monitoring these symptoms early on is crucial for timely intervention and support strategies.
Causes of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is primarily caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene. This gene is responsible for producing dystrophin, a protein essential for maintaining muscle cell structure.
When this gene mutates, it results in little or no production of dystrophin. Without sufficient levels of this protein, muscle cells become damaged and progressively weaken over time.
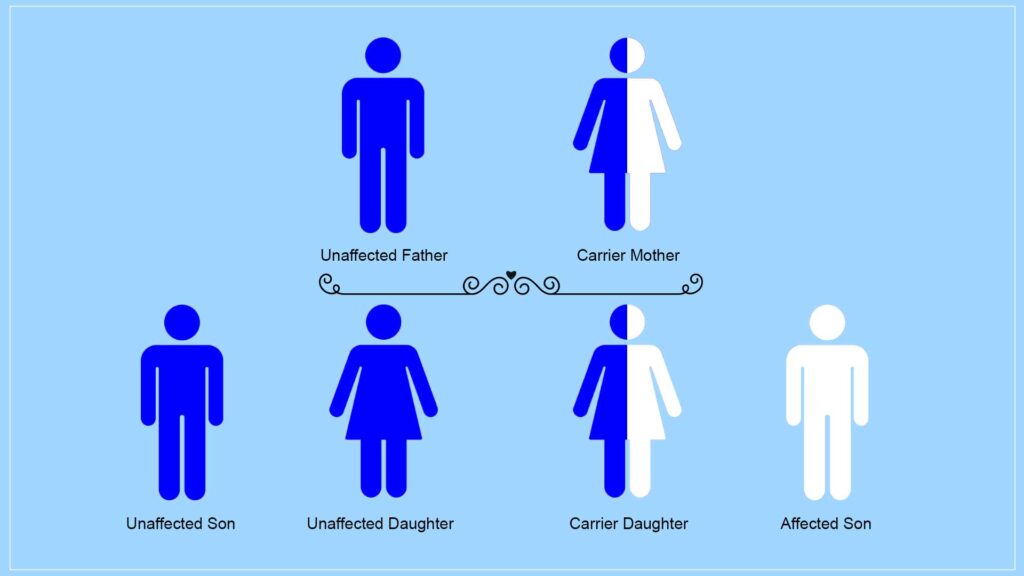
The condition follows an X-linked recessive pattern. This means that males are more frequently affected because they have only one X chromosome. Females can be carriers but typically do not show symptoms due to having two X chromosomes.
Environmental factors may also play a role, although genetics remain the main contributors. Research continues to explore additional influences that might exacerbate or mitigate the severity of DMD symptoms as patients age. [Read More: Genetic Causes of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy]
Diagnosing Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Diagnosing Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) involves a series of evaluations. A pediatrician usually begins with a thorough physical examination and reviews the child’s medical history.
Doctors often look for signs such as muscle weakness, difficulty walking, or delays in motor skills. Parents may notice that their child has trouble running or climbing stairs.
Blood tests play a crucial role in diagnosis. Elevated levels of creatine kinase (CK) can indicate muscle damage, which is common in DMD.
If initial tests suggest DMD, genetic testing confirms the diagnosis by identifying mutations in the dystrophin gene.
Additionally, imaging studies like MRI might be used to assess muscle condition further. Each step helps create an accurate picture of the child’s health and guides future management plans effectively. [Read More: Does My Child Have Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD)?]
Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Treatment options for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to slow muscle degeneration. These medications can enhance strength and prolong the ability to walk.
Physical therapy plays a vital role in maintaining mobility. Regular exercises help keep muscles flexible and prevent contractures. Occupational therapy is also beneficial, assisting individuals with daily activities.
In some cases, heart medications may be necessary as DMD can affect cardiac health. Monitoring heart function becomes crucial as the disease progresses.
Emerging treatments include gene therapies aimed at addressing the underlying genetic causes of DMD. Clinical trials are exploring innovative approaches that hold promise for future advancements. [Learn More: Cures of Duchenne (List of All Researches)]
Assistive devices, like wheelchairs or braces, offer support and improve independence for those affected by this condition. Careful management ensures that individuals with DMD lead fulfilling lives despite their challenges.
Management and Treatment
Managing Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy focuses on maximizing the quality of life for those affected. Health care teams often include neurologists, physical therapists, and occupational therapists. Together, they create a personalized treatment plan.
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in maintaining mobility and flexibility. Regular exercises can help strengthen muscles and prevent contractures.
Medications may also be prescribed to manage symptoms and slow disease progression. Corticosteroids are commonly used to enhance muscle strength and function.
Assistive devices like braces or wheelchairs can improve independence as mobility decreases over time. These tools provide necessary support for daily activities.
Regular monitoring is vital to adapt treatments as needed throughout various stages of the condition. Support from family members is essential in fostering an environment that promotes emotional well-being while facing challenges associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Prevention
Preventing Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) poses significant challenges due to its genetic nature. This condition is primarily caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene, which are inherited from parents. Because of this hereditary aspect, there’s no established method for prevention.
However, couples with a family history of DMD can consider genetic counseling. This service provides insight into potential risks and options during pregnancy or assisted reproductive technology. Parents may choose preimplantation genetic diagnosis to screen embryos for the mutation before implantation.
Awareness campaigns also play a crucial role in education about muscular dystrophies and their implications. Increased understanding can lead to early detection and intervention strategies that improve quality of life even if prevention isn’t possible.
Research continues to explore new avenues for preventing or delaying the onset of symptoms associated with DMD through innovative therapies and gene editing techniques, giving hope for future advancements in this field.
Prognosis and Outlook
The prognosis for individuals with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) varies widely. Typically, the disease progresses rapidly, leading to significant muscle weakness and loss of mobility by adolescence. Most boys diagnosed with DMD will require wheelchair assistance in their early teens.
As the condition advances, respiratory and cardiac issues often emerge. These complications can significantly impact life expectancy. However, advancements in medical care have improved outcomes for many patients.
Early intervention plays a crucial role in enhancing quality of life. Regular physical therapy and use of corticosteroids may slow down deterioration.
Many young adults are now reaching their twenties or thirties due to better management strategies and supportive technologies. Ongoing research offers hope for new treatments that could alter the course of this challenging condition significantly.
Living With Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Living with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) presents daily challenges that require adaptability and resilience. Individuals often experience muscle weakness that progresses over time, affecting mobility and independence.
Daily routines may involve specialized physical therapy to maintain strength and flexibility. Assistive devices like wheelchairs or braces can offer support, making movement easier. Many families find it helpful to create a structured schedule that balances activities with rest periods.
Emotional well-being is equally important. Support groups provide a sense of community where individuals and their families share experiences and coping strategies. Finding hobbies or interests can also promote joy amid the difficulties.
Educational needs must be addressed as well. Schools should implement individualized education plans (IEPs) to cater to learning styles while accommodating physical limitations.
Engagement in advocacy efforts helps raise awareness about DMD, fostering connections among those affected by this condition within society as a whole.
Resources and Support
Navigating life with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy can be challenging, but numerous resources and support systems are available. Various organizations provide valuable information on managing the condition, ranging from medical advice to emotional support.
The Muscular Dystrophy Association (MDA) offers educational materials, advocacy programs, and community events. They also fund research to advance treatment options. The Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy (PPMD) is another vital resource that focuses on raising awareness and funding for innovative therapies.
Support groups play a crucial role in connecting families facing similar challenges. These gatherings allow individuals to share experiences and coping strategies, creating a sense of community. Online forums can also serve as platforms where people exchange advice and encouragement without geographical barriers.
Additionally, healthcare professionals specializing in neuromuscular disorders offer tailored guidance for patients and their families. Accessing these resources can significantly improve quality of life while fostering hope for advancements in care.
Research and Clinical Trials
Research into Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is vibrant and ongoing. Scientists are exploring various therapeutic approaches to combat this genetic disorder. Gene therapy, which aims to repair or replace the defective dystrophin gene, shows promising results in early trials.
Clinical trials play a crucial role in developing new treatments for DMD. These studies assess potential therapies’ safety and effectiveness before they receive approval for wider use. Patients can often participate in these trials, contributing valuable data that may lead to breakthroughs.
Researchers are also investigating existing medications that could alleviate symptoms or slow disease progression. Collaboration between universities, biotech companies, and patient advocacy groups amplifies efforts toward finding viable solutions.
With advancements in technology like CRISPR gene editing, hope grows for innovative treatments on the horizon. The commitment of scientists worldwide fuels optimism among families affected by Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.
Advocacy and Community
Living with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) can be challenging, but a strong community is vital for support. Advocacy groups play an essential role in raising awareness about the disease. Organizations like Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy and Muscular Dystrophy Association are at the forefront of research funding and policy changes.
These communities offer resources that make a difference in everyday life. They provide access to information on emerging treatments, assistive technologies, and educational materials for families affected by DMD. Connecting with others who understand your journey can also alleviate feelings of isolation.
Participating in local or national events helps raise funds for research while fostering connections among families facing similar challenges. Support networks often organize workshops, conferences, and social activities that promote sharing experiences and strategies for managing daily hurdles.
Engaging in advocacy efforts increases visibility around Duchenne muscular dystrophy, encouraging more people to learn about its impact. By joining forces within these communities, individuals can contribute to meaningful change that benefits all those living with this condition.
Together, we can ensure that no one walks alone on this path—empowering each other through education, shared experiences, and unwavering support as we navigate life with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.




[…] After a 3-4 month wait, our genetic test results came in. Our little son had Duchenne (DMD). […]
[…] For individuals with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), adults and children six years of age and older, the U.S. has approved the oral treatment duvyzat (givinostat). It was created by Italfarmaco with the intention of reducing DMD patients’ inflammation and muscle atrophy, ultimately slowing the disease’s progression. [Read more: What is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy?] […]
السلام عليكم ورحمة الله وبركاته،
أتقدم إليكم بهذا الطلب الإنساني العاجل راجياً منكم النظر في حالة ابني يوسف الحاتمي، الذي يُعاني من مرض نادر وخطير يُعرف بـ متلازمة دوشين، وهو مرض عضلي يُصيب الأطفال ويتطور بسرعة ليؤثر على الحركة والتنفس، وقد يؤدي للأسف إلى مضاعفات خطيرة تهدد الحياة.
تكلفة العلاج الذي يحتاجه يوسف تفوق 50 مليون سنتيم، وهو مبلغ كبير يفوق قدرتنا تمامًا كعائلة فقيرة لا تملك أي مورد مالي لتأمين هذا العلاج الضروري.
أتوجه إليكم بقلبي كله أمل أن تساعدونا، سواء بالتكفل بعلاج يوسف، أو توجيهنا إلى من يمكنه دعمه من المحسنين أو الجهات المختصة.
أنا مستعد لتقديم جميع الوثائق والتقارير الطبية التي تثبت الحالة، ومستعد أيضًا للتواصل في أي وقت.
أرجوكم، لا تتركونا وحدنا في هذا الظرف الصعب، فابني في حاجة ماسة لإنقاذ حياته.
جزاكم الله عنا كل خير.
[…] A genetic condition known as Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) results in gradual muscle weakening. Boys are more likely to have DMD, with symptoms first appearing in early childhood. DMD has no known treatment. Medical professionals use physical therapy, steroids, and assistive technology (wheelchairs, braces, etc.) to treat symptoms. Targeting the aberrant gene, new medications are being researched to help reduce the progression of DMD. A newly developed gene therapy medication called Elevidys helps maintain muscular strength in people with DMD. [Read more: What is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy?] […]
[…] The excitement you feel until your child is born continues to increase until the day he/she is born. After birth, we may also experience some anxiety. There is nothing physically wrong with the child and he/she was born very healthy. However, if minor problems begin to appear in the child’s development in the future and the family does not follow these problems carefully, there may be a delay in the diagnosis of some diseases. The name of the disease that comes first in this situation is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD). [Read More: What is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy?] […]
je niekde registrácia s pompcoi detom s DMD?
Žiaľ, slovenské spolky sa nám zatiaľ neozvali. Preto nevieme. 🙁