Duchenne Exon 51 skipping therapies are innovative treatments aimed at addressing the genetic mutation responsible for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). By skipping exon 51 in the dystrophin gene, these therapies help produce a shorter, functional version of the dystrophin protein, potentially slowing disease progression and improving quality of life for patients. This cutting-edge approach offers hope for DMD patients, focusing on enhancing muscular function and prolonging mobility.
Table of Contents
About Duchenne
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe genetic disorder that primarily affects boys and leads to progressive muscle weakness, loss of mobility, and eventually, respiratory and cardiac complications. DMD is caused by mutations in the DMD gene, which encodes dystrophin, a critical protein that stabilizes muscle cell membranes. Without dystrophin, muscle fibers are more prone to damage during contraction, leading to muscle degeneration and the hallmark symptoms of DMD.
Exon 51 Skipping Therapies
The main genetic mutation in DMD is deletions of specific exons in the DMD gene, disrupting the production of functional dystrophin. One approach to treating DMD is exon skipping, a therapeutic strategy that aims to bypass defective parts of the gene to allow for the production of a truncated, but partially functional, dystrophin protein. Exon 51 skipping is one of the most studied exon-skipping therapies, offering hope to a significant subgroup of DMD patients. (What is Exon Skipping?)
What is Exon 51 Skipping?
The DMD gene consists of 79 exons, and mutations in this gene commonly involve the deletion of specific exons. These deletions typically result in a frameshift that prevents the production of dystrophin. Exon 51 skipping involves using antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) to mask the mutated exon and promote the “skipping” of that exon during the splicing process of RNA. By skipping exon 51, the downstream exons can be joined together, restoring the reading frame and allowing the production of a shorter but functional form of dystrophin.
This strategy is aimed at restoring a functional dystrophin protein that can somewhat compensate for the lack of normal dystrophin, potentially reducing disease progression and improving muscle function in patients who have deletions amenable to exon 51 skipping. (Read More: What is Exon Deletion in DMD?)
FDA-Approved Exon 51 Skipping Therapies
EXONDYS 51 (eteplirsen)
EXONDYS 51 (eteplirsen) is the first FDA-approved Duchenne muscular dystrophy treatment for patients who have a confirmed genetic mutation in the dystrophin gene that can be treated by skipping exon 51. In some patients, it helps the body make a shorter form of the dystrophin protein. (Learn More: Eteplirsen)
EXONDYS 51 (eteplirsen) was not approved by the European Medicines Agency. (EMA)
Which Deletions are Amenable to Exon 51 Skipping?
Exon 51 skipping is specifically designed for patients who have deletions in the exons in the DMD gene, which you can see below. These deletions are amenable to exon 51 skipping, as skipping this exon restores the reading frame of the gene, resulting in the production of a shortened, but functional, dystrophin protein.
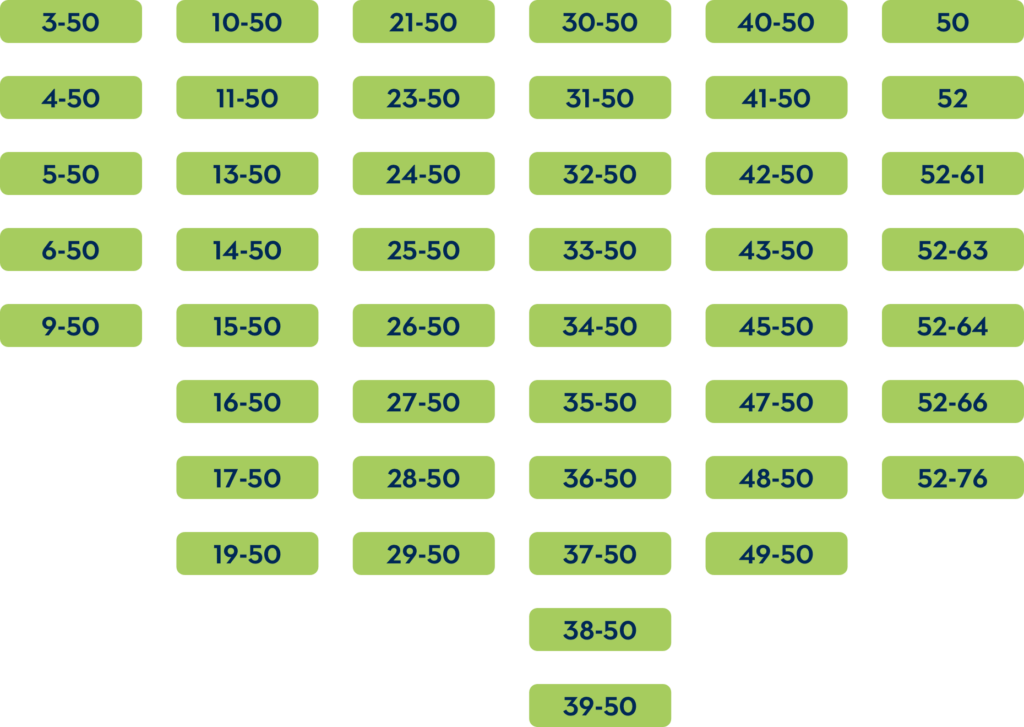
Research has shown that a significant proportion of DMD patients (about 13-15%) have deletions that are amenable to exon 51 skipping. These deletions typically affect a critical part of the DMD gene, resulting in the loss of dystrophin functionality. By skipping exon 51, these patients can produce a modified form of dystrophin that can potentially preserve muscle integrity, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life.
It is important to note that exon 51 skipping is only effective for certain genetic mutations, and patients must undergo genetic testing to determine if they are suitable candidates for exon 51-based therapies. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) and gene sequencing technologies have made it easier to identify these deletions and assess their amenability to exon skipping therapies.
Clinical Trials for Exon 51 Skipping Therapies
While exon 51 skipping therapies represent a significant advancement in the treatment of DMD, several challenges remain. The effectiveness of exon skipping therapies in terms of long-term benefits and functional improvements is still being studied. Additionally, patient response variability—including the extent to which dystrophin is produced and how it translates to functional improvements—poses an ongoing challenge.
Here are the promising exon 51 skipping studies:
Dyne Therapeutics – DYNE-251
DYNE-251 is an investigational therapeutic being evaluated in the Phase 1/2 global DELIVER clinical trial for people living with DMD who are amenable to exon 51 skipping. (Read More: DYNE-251)
Jiao Tong University – LE051
Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine has announced a clinical trial to evaluate the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of a single intravenous infusion of LE051 in patients with DMD amenable to exon 51 skipping. (Read More: LE051)
BioMarin Pharmaceutical – BMN 351
BMN 351 is a next generation of antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) therapy for boys with exon 51 amenable DMD. ASOs are drugs that affect how cells make certain proteins. They are being used to treat many different types of genetic health conditions. BMN 351 is an investigational medicine, which means it has not been found to be safe and effective in people and has not been approved for use outside of clinical trials. (Read More: BMN 351)
Entrada Therapeutics – ENTR-601-51
ENTR-601-51, an investigational therapy for the potential treatment of people living with Duchenne who are exon 51 skipping amenable, is being evaluated for its potential to restore the mRNA reading frame and allow for the translation of dystrophin protein that is slightly shortened but still functional. (Read More: ENTR-601-51)
Conclusion
Exon 51 skipping therapies represent a promising therapeutic approach for DMD, offering hope for patients with specific mutations that are amenable to this technique. While the long-term functional benefits are still under investigation, exon 51 skipping therapies mark an exciting step forward in the fight against Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Continued research, long-term clinical trials, and further advances in genetic testing and personalized medicine will be crucial in optimizing these therapies and expanding their use to more DMD patients in the future.
Learn More: Cures of Duchenne (List of All Researches)



